UaSource
Large scale ice-flow model
This project is maintained by GHilmarG

Úa is a finite-element ice-flow model developed at the University of Northumbria, Newcastle, UK, by Hilmar Gudmundsson
A week-long international user meeting and workshop is held annually, usually in early June.
Examples of simulations using this code can be found in our YouTube channel.
Installation
The flow model is MATLAB based and you will need a MATLAB installation to run it.
Installing Úa is simple: Just download/clone the code from github. Put all the files into one folder and make sure that this folder is on the MATLAB path.
You can then test if it runs by writing
Ua [Ret]
in the MATLAB command line, and you are done! Úa is installed!
You will then find the documentation for Úa to be a part of the MATLAB documentation system where Úa appears as a separate toolbox.
If you want to be able to run Úa from another folder than just the installation folder (a good idea) then you need to add the source folder to the MATLAB path. You can, for example, set the path as:
addpath(genpath('MyUaSourceFileFolder'))
So for example if you have cloned the source directory from github into a local folder on your own computer with the name:
C:\Users\Hilmar\Ua\UaSource
then add that folder to the MATLAB path as:
addpath(genpath('C:\Users\Hilmar\Ua\UaSource'))
No special toolboxes are required, however, some optional features can only be used with toolboxes such as the Optimisation and the Machine Learning toolboxes.
To set up your own runs you should also download the Examples which are in a separate repository. Download this into another folder, and then you will have several different subfolders, each containing a particular example of a model setup.
Note: Úa uses the mesh generator ‘mesh2d’ and no further steps are required if you just want to use that mesh generator. However, one can optionally also use the well-known mesh generator Gmsh which then must be installed separately.
Cloning from GitHub: There are many different ways of copying/cloning a repository from GitHub. You can for example download it as zip file. While not strictly necessary, it is presumably best to have git installed locally. You can install git from:
https://git-scm.com/downloads
You can the write on the git command line:
git clone https://github.com/GHilmarG/UaSource.git
Brief model description.
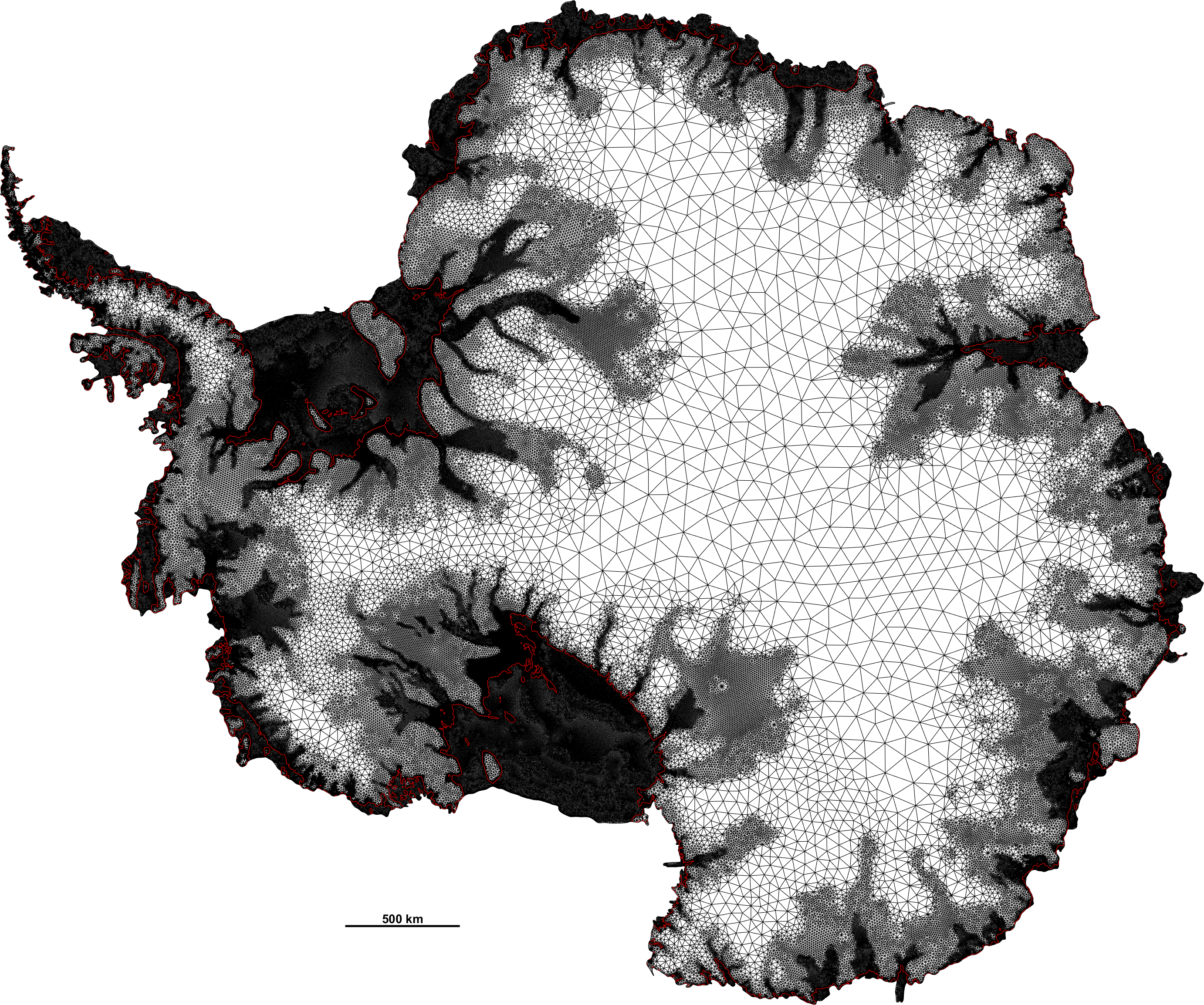
The model is based on a vertically integrated formulation of the momentum equations and can be used to simulate the flow of large ice sheets such as the Antarctic and the Greenland Ice Sheets, ice caps and mountain glaciers.
The ice-flow equations are solved on an unstructured mesh consisting of linear, quadratic or cubic triangular elements. Various meshing options are available, including automated mesh refinement and coarsening. When simulating the flow of marine ice sheets these meshing options allow, for example, the areas around grounding lines to be automatically highly resolved as the grounding-lines migrate through the computational domain. Elements can be activated and deactivated. This enables the computational domain itself to change in the course of a run, for example when simulating the growth and decay of a large group of mountain glaciers.
Inversion for model parameters is done using the adjoint method. Both Bayesian and Tikhonov formulations are supported, and the inversion can be done over either nodes or elements.
Ice-thickness positivity is enforced using the active set-method.
Forward time integration can be done in a fully coupled manner, and the resulting non-linear system is solved using the Newton-Raphson method.
A technical manual, the Úa Compendium, provides a description of various mathematical and technical aspects of the model.
External mesh generator
If in addition to ‘mesh2d’ you also want to use the external mesh generator `gmsh’ then define the MATLAB environmental variable ‘GmshHomeDirectory’ as:
setenv('GmshHomeDirectory','MyDrive/Ua/Source/gmsh-4.4.1-Windows')
Running Úa
You run Ua from the MATLAB command line by writing:
Ua [Ret]
All run-specific input files should be in the local directory.
Getting help
You can get help on the use of Úa in the same way as you would get help on various in-build MATLAB commands by writing
help Ua
in the MATLAB command line, or
doc Ua
Most m-files that are part of the Úa program have some inbuilt help text, for example try
doc Ua2D_DefaultParameters
Ice-Ocean coupling
Úa has been coupled with the ocean circulation model MITgcm (ÚaMIT), an ocean plume model (ÚaPICO), and the ocean circulation model Fesom (ÚaFesom).
Recent Papers
Naughten, K. A., De Rydt, J., Rosier, S. H. R., Jenkins, A., Holland, P. R., & Ridley, J. K. (2021). Two-timescale response of a large Antarctic ice shelf to climate change. Nature Communications, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-22259-0
Jones, R. S., Gudmundsson, G. H., Mackintosh, A. N., McCormack, F. S., & Whitmore, R. J. (2021). Ocean‐Driven and Topography‐Controlled Nonlinear Glacier Retreat During the Holocene: Southwestern Ross Sea, Antarctica. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(5), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL091454
De Rydt, J., Reese, R., Paolo, F. S., & Gudmundsson, G. H. (2021). Drivers of Pine Island Glacier speed-up between 1996 and 2016. The Cryosphere, 15(1), 113–132. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-15-113-2021
Rosier, S. H. R., Reese, R., Donges, J. F., De Rydt, J., Gudmundsson, G. H., & Winkelmann, R. (2021). The tipping points and early warning indicators for Pine Island Glacier, West Antarctica. The Cryosphere, 15(3), 1501–1516. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-15-1501-2021
Hill, E. A., Gudmundsson, G. H., Carr, J. R., Stokes, C. R., & King, H. M. (2020). Twenty-first century response of Petermann Glacier, northwest Greenland to ice shelf loss. Journal of Glaciology, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2020.97
Ranganathan, M., Minchew, B., Meyer, C. R., & Gudmundsson, G. H. (2020). A new approach to inferring basal drag and ice rheology in ice streams, with applications to West Antarctic Ice Streams. Journal of Glaciology, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1017/jog.2020.95
De Rydt, J., Gudmundsson, G. H., Nagler, T., & Wuite, J. (2019). Calving cycle of the Brunt Ice Shelf, Antarctica, driven by changes in ice shelf geometry. The Cryosphere, 13(10), 2771–2787. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-13-2771-2019
Gudmundsson, G. H., Paolo, F. S., Adusumilli, S., & Fricker, H. A. (2019). Instantaneous Antarctic ice sheet mass loss driven by thinning ice shelves. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(23), 13903–13909. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL085027
De Rydt, J., Gudmundsson, G. H., Nagler, T., Wuite, J., & King, E. C. (2018). Recent rift formation and impact on the structural integrity of the Brunt Ice Shelf, East Antarctica. The Cryosphere, 12(2), 505–520. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-12-505-2081
Reese, R., Gudmundsson, G. H., Levermann, A., & Winkelmann, R. (2018). The far reach of ice-shelf thinning in Antarctica. Nature Climate Change, 8(1), 53–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-017-0020-x
Reese, R., Winkelmann, R., & Gudmundsson, G. H. (2018). Grounding-line flux formula applied as a flux condition in numerical simulations fails for buttressed Antarctic ice streams. The Cryosphere, 12(10), 3229–3242. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-12-3229-2018